Adaptability, a coveted soft skill in the job market, encompasses the ability to respond flexibly to evolving factors, conditions, or environments by acquiring new skills.
Given the inherent unpredictability of every industry, adaptability is crucial for businesses and employees to swiftly navigate unforeseen challenges.

Business adaptability vs personal adaptability
Business adaptability primarily relates to how an organization adjusts its strategies, operations, and structures in response to external market dynamics and industry shifts.
Meanwhile, personal adaptability focuses on how employees adapt their behaviors, skills, and approaches to excel within their specific job roles and work environment.
Below is a breakdown of how the two types of adaptability differ.
Business adaptability
- Driven by market changes, competition, regulatory changes, technological advancements, and economic trends.
- Organizations must adapt to remain competitive and sustainable, developing business resilience.
- Requirements include strategic planning, risk management, market awareness, and supply chain resilience. For example, Decathlon Coppola told McKinsey: ‘We’ve been able to thrive because of our ability to adapt to local markets. As a global business, we are very agile. We adjust to local demands in real-time.’
- Impact is measured on financial performance, workforce optimization, and sustainability in a competitive marketplace.
Personal adaptability
- Driven by changes in job responsibilities, work processes, career aspirations, and personal development goals.
- People must adapt to changing workplaces to excel and progress in their careers.
- Requirements include developing soft skills such as resilience, flexibility, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence.
- The impact is measured by job performance, career progression, job satisfaction, and ability to contribute positively towards business success.
What soft skills indicate personal adaptability?
Resilience
The ability to bounce back from setbacks, adversity, and stress. It allows individuals to maintain their composure and motivation in facing challenges and recover quickly from setbacks.
Example: An employee faces criticism for a project they’ve been working on. Instead of getting discouraged, they take the feedback constructively, make necessary improvements, and continue to work diligently.
Flexibility
Being open to change and willing to adjust one’s approach or mindset when necessary. Adaptable individuals can easily pivot and embrace new ways of thinking or doing things.
Example: A team is restructured, and employees are asked to take on new responsibilities outside their usual roles. They adapt willingly and quickly to the new tasks, demonstrating their flexibility.
Problem-solving
The ability to analyze situations, identify potential solutions, and make effective decisions, even in unfamiliar or rapidly changing contexts.
Example: When a production line encounters an unexpected issue, an employee quickly analyzes the problem, identifies the root cause, and develops a solution to minimize downtime.
Emotional intelligence
Recognizing and understanding one’s own emotions and the emotions of others. It helps individuals navigate interpersonal dynamics and build strong relationships, which is essential in adapting to various workplace scenarios.
Example: A manager notices a team member seems upset and takes the time to have a private conversation, empathizing with their concerns and offering support.
Communication
Conveying ideas, listening to others, and collaborating effectively. Adaptable individuals can communicate their needs, ideas, and feedback clearly and adapt their communication style as needed.
Example: During a team meeting, employees clearly articulate their ideas and actively listen to others, fostering effective collaboration and problem-solving.
Stress management
Managing stress and maintaining composure in high-pressure situations is vital for personal adaptability. It helps individuals stay productive and focused when facing challenges.
Example: Despite facing tight project deadlines and a heavy workload, an employee stays calm and organized, managing stress effectively to deliver quality work.
Time management
Enables individuals to prioritize tasks, set goals, and effectively allocate their time, ensuring they can adapt to changing priorities and meet deadlines.
Example: An employee efficiently prioritizes tasks, creating a schedule that allows them to meet project deadlines while maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
Decision-making
Assessing options, weighing pros and cons, and making informed choices. Adaptability often requires making quick decisions in uncertain situations.
Example: Faced with two viable options for a business strategy, a manager carefully assesses the pros and cons of each and confidently makes a well-informed decision.

What makes a business adaptable?
Talent development
Investing in employee training and development builds a skilled and adaptable workforce. Employees with diverse skill sets are better prepared to tackle evolving challenges.
Example: A manufacturing company invests in upskilling its workforce by providing training programs in automation and data analytics. This enables employees to assume new roles as the company automates certain processes.
Technology adoption
Embracing cutting-edge technologies can enhance efficiency and provide insights that inform strategic decisions. Technology can also facilitate remote work and adaptability in the face of external disruptions.
Example: A retail chain implements an AI-powered inventory management system that uses data analytics to optimize stock levels and distribution, allowing the company to quickly adjust to fluctuations in demand.
Strategic planning
Regularly reviewing and adjusting the business strategy to align with changing market conditions and customer needs is crucial. This may involve diversifying products or services, entering new markets, or changing business models.
Example: A fast-food restaurant chain adds healthier menu options in response to changing consumer preferences for healthier eating, aligning its strategy with evolving customer needs.
Risk management
Developing risk management strategies helps the organization anticipate and mitigate potential threats. This includes financial risk, cybersecurity risk, and market risk.
Example: A financial institution implements a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, including regular vulnerability assessments and employee training, to mitigate the risk of cyberattacks.
Market awareness
Staying informed about industry trends, market dynamics, and competitive landscapes enables the organization to proactively respond to shifts in the business environment.
Example: An automobile manufacturer actively monitors developments in electric vehicle technology and invests in electric vehicle production to remain competitive in a shifting automotive market.
Supply chain resilience
Ensuring a resilient supply chain that can adapt to disruptions is crucial. Diversifying suppliers and having contingency plans in place can mitigate risks.
Example: A pharmaceutical company diversifies its sources of raw materials and establishes backup suppliers to ensure a steady supply chain, reducing the impact of disruptions.
Financial flexibility
Maintaining a strong financial position with access to capital or credit facilities provides the resources needed to invest in adaptability strategies when necessary.
Example: A small business maintains a line of credit that can be tapped into during economic uncertainty, ensuring it has the financial resources needed to weather downturns.

Adaptability vs change management
Being able to adapt means something slightly different from being able to manage change.
Here is how adaptability and change management differ.
Adaptability
- Refers to an individual’s or organization’s ability to adjust, evolve, and thrive in response to various changes, challenges, and evolving circumstances.
- An ongoing quality that enables flexibility and resilience in the face of both expected and unexpected developments.
- Focused on building a foundation for the long-term ability to navigate change effectively. The mindsets and skills developed can be used in various contexts.
Change management
- Refers to a specific and structured process an organization rolls out to plan, implement, and monitor changes, often to achieve a specific outcome
- Managing a particular change initiative. It involves defining a change, creating a plan, communicating it, and addressing resistance to ensure a smooth transition.
- Guiding and supporting individuals and teams through a specific change, minimizing disruptions, and maximizing the chances of successful implementation.
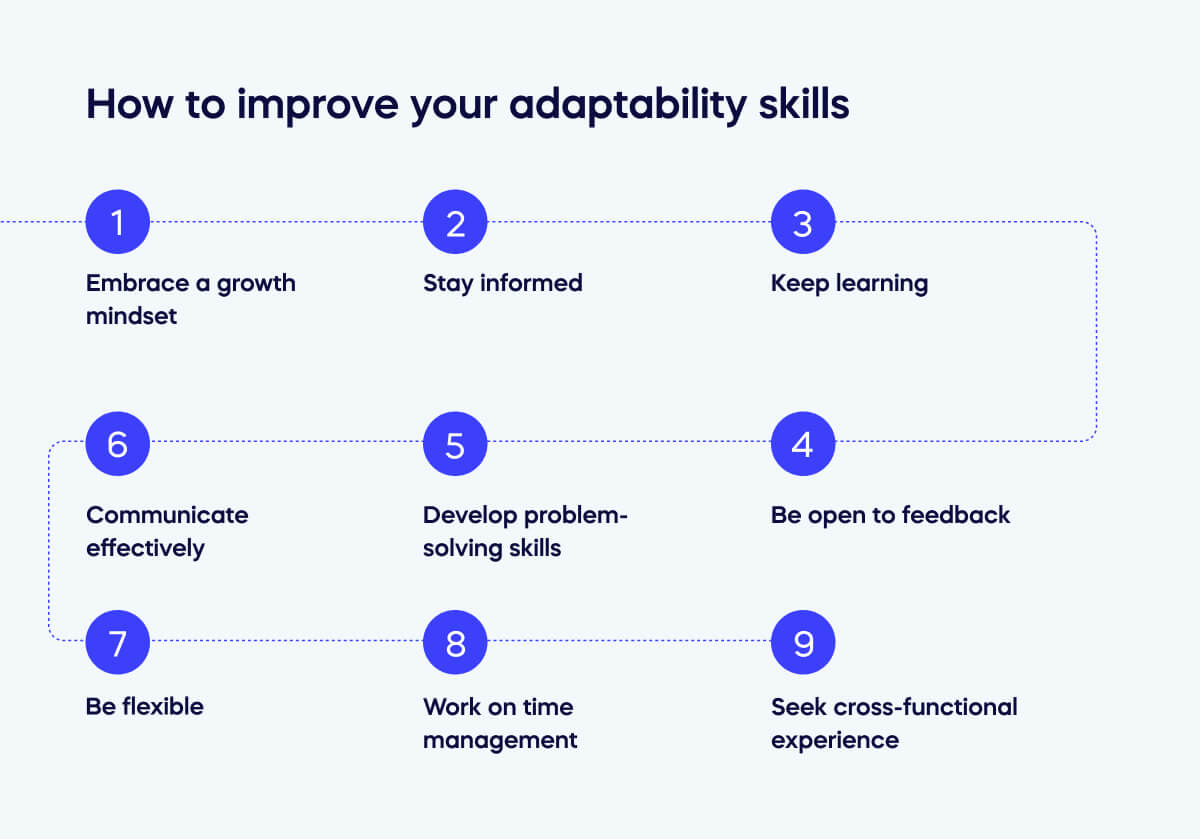
How to improve your adaptability skills
Improving adaptability skills in the workplace is essential for personal and professional growth, so consider the following:
Embrace a growth mindset
Cultivate a belief that your abilities and intelligence can be developed with effort and learning. A growth mindset fosters a willingness to take on challenges and see setbacks as opportunities for growth.
Stay informed
Regularly update your knowledge about your industry, trends, and emerging technologies. Being well-informed allows you to anticipate changes and adapt proactively.
Keep learning
Seek out opportunities for learning and skill development, such as workshops, courses, online resources, and mentorship programs.
Be open to feedback
Welcome constructive feedback as a means of personal growth. Use feedback to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments.
Develop problem-solving skills
Hone your problem-solving abilities by analyzing situations, breaking down complex issues, and finding practical solutions.
Communicate effectively
Practice clear and open communication with colleagues and supervisors. Effective communication is vital for collaboration and adapting to changing work environments.
Be flexible
Be willing to adjust your plans and strategies when necessary. Flexibility allows you to respond quickly to unexpected changes.
Work on time management
Improve your time management skills to prioritize tasks and allocate your time efficiently. This helps you handle multiple responsibilities and adapt to shifting priorities.
Seek cross-functional experience
Seek opportunities to work on cross-functional teams or take on roles outside your primary expertise. This broadens your skill set and adaptability.