Contextual AI, or Contextual Artificial Intelligence, refers to an artificial intelligence system that can understand and respond to input in a way that considers the context in which the input is given.
This context may include factors such as the user’s previous interactions, the current situation, the environment, and other relevant information.
Contextual AI systems are designed to provide more relevant and personalized responses, as they can adapt their behavior based on the specific context of the interaction.
They often use natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), and other AI techniques to analyze and interpret the context of a conversation or task.
This enables them to provide more meaningful and tailored responses, particularly useful in applications such as virtual assistants, customer support chatbots, recommendation systems, and personalized content delivery.
For example, a contextual AI-powered virtual assistant can understand and respond to users’ requests with knowledge of their previous conversations, location, and preferences, delivering a more personalized and helpful experience.
The ability to consider context makes these AI systems more versatile and capable of handling a wide range of tasks and interactions in a more human-like manner.
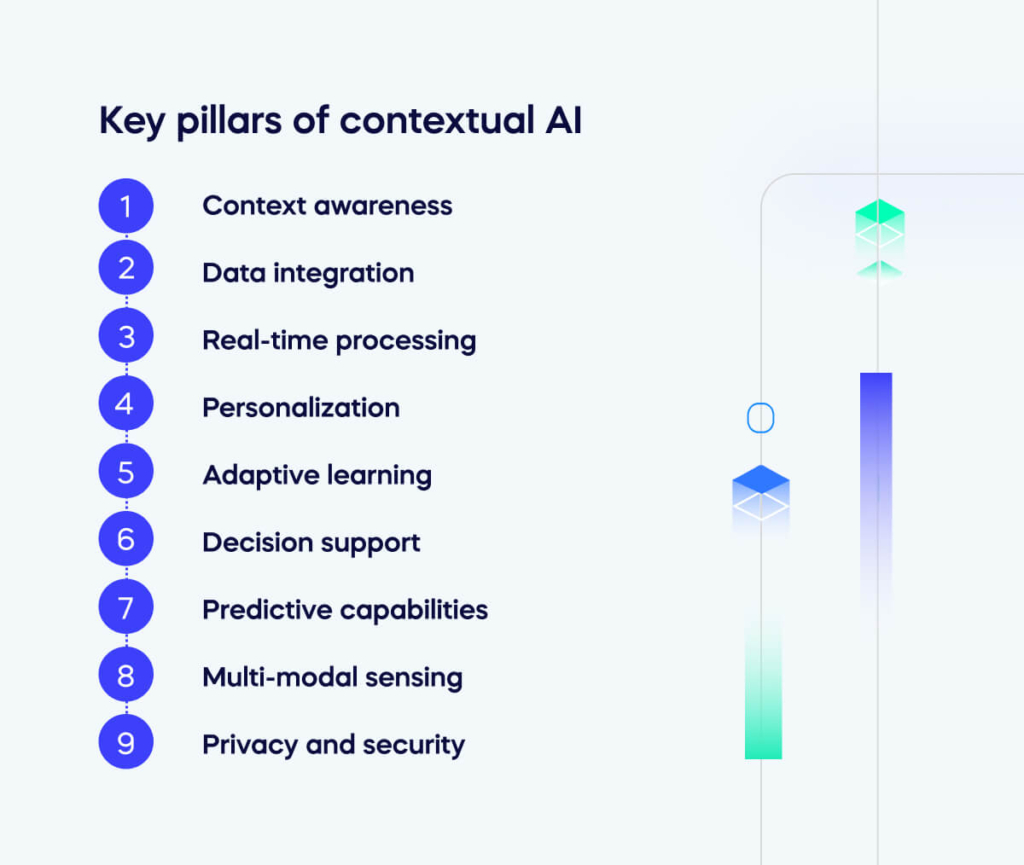
Key pillars of contextual AI
The key pillars of contextual AI include:
Context awareness
Understanding and interpreting the context within which they operate is fundamental to contextual AI. This encompasses user information, environmental conditions, time, and other relevant elements. Users benefit from more pertinent and individualized responses and actions.
Data integration
Contextual AI heavily relies on amalgamating data from different sources to holistically comprehend the situation. This includes data from sensors, IoT devices, social media, and various other inputs. Well-informed decisions can subsequently be made based on a comprehensive context.
Real-time processing
Often operating in real-time, contextual AI continuously observes and analyzes the evolving context. As a result, the AI can promptly adapt to new information and respond in a timely manner.
Personalization
Customizing interactions and recommendations according to an individual user’s preferences, behaviors, and historical data is a core feature of contextual AI.
Adaptive learning
Contextual AI systems can learn and adjust to shifting contexts and user behaviors over time. Machine learning and predictive analytics are frequently employed.
Decision support
The technology can assist users and organizations in making improved decisions by furnishing insights and recommendations grounded in the present context. This is particularly valuable in healthcare, finance, and business domains.
Predictive capabilities
Contextual AI can predict future events or trends by leveraging historical data and the current context. Predictive analytics is commonly employed to anticipate user needs and preferences.
Multi-modal sensing
Contextual AI can combine information from various senses, including text, speech, images, and video, to better understand and respond to the context. This is especially critical in applications like autonomous vehicles, healthcare, and augmented reality.
Privacy and security
In light of the extensive data collection and analysis associated with contextual AI, safeguarding user data and ensuring responsible usage are crucial. Maintaining user trust and adhering to regulatory requirements hinges on robust privacy and security measures.
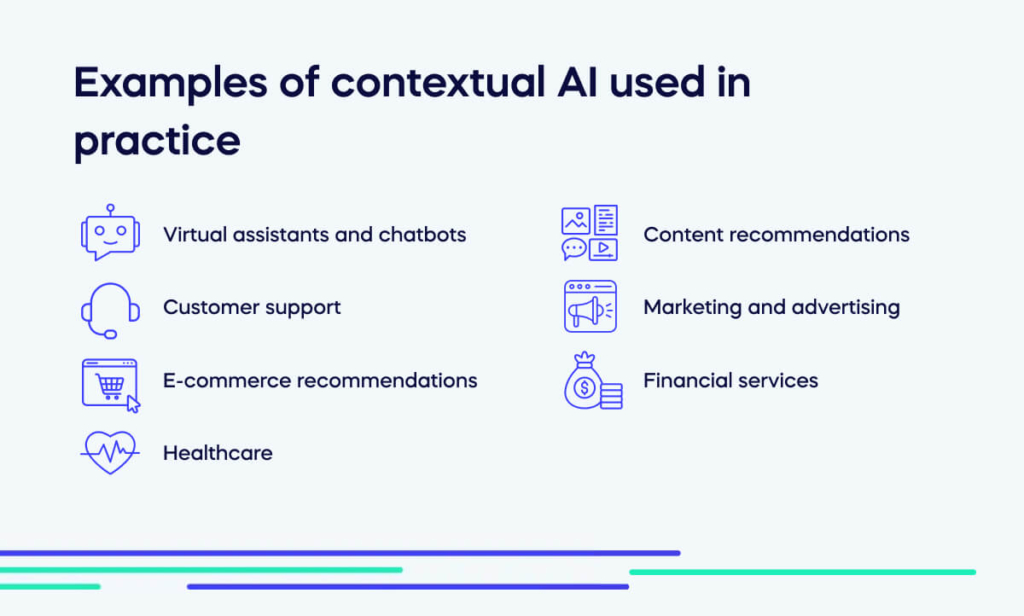
Examples of contextual AI used in practice
Contextual AI is used in various practical applications across industries to enhance user experiences, improve decision-making, and automate tasks efficiently. Here are some examples of contextual AI in practice:
Virtual assistants and chatbots
Virtual assistants like Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri, and chatbots on websites and messaging platforms use contextual AI to understand and respond to user queries based on the context of the conversation, user preferences, and past interactions.
Customer support
Many companies use contextual AI in their customer support systems to provide personalized assistance. For example, when you contact customer support, the system may analyze your purchase history and prior interactions to offer more relevant solutions or escalate your issue appropriately.
E-commerce recommendations
Online retailers employ contextual AI to provide product recommendations based on a user’s browsing and purchase history. The system can take into account the user’s current session, location, and other factors to suggest the most relevant items.
Healthcare
In healthcare, contextual AI is used for clinical decision support. Electronic health record systems can analyze a patient’s medical history and current symptoms to assist physicians in making diagnoses and treatment recommendations.
Content recommendations
Streaming platforms like Netflix and YouTube employ contextual AI to recommend content to users based on their viewing history, preferences, and habits, enhancing the user experience.
Marketing and advertising
Contextual AI is used in digital advertising to target ads to the right audience at the right time based on user behavior, demographics, and browsing history. Advertisers can deliver more relevant and personalized content.
Financial services
In the financial industry, contextual AI is used for fraud detection, credit scoring, and personalized financial advice. It can assess a user’s economic behavior and history to make lending or investment recommendations.
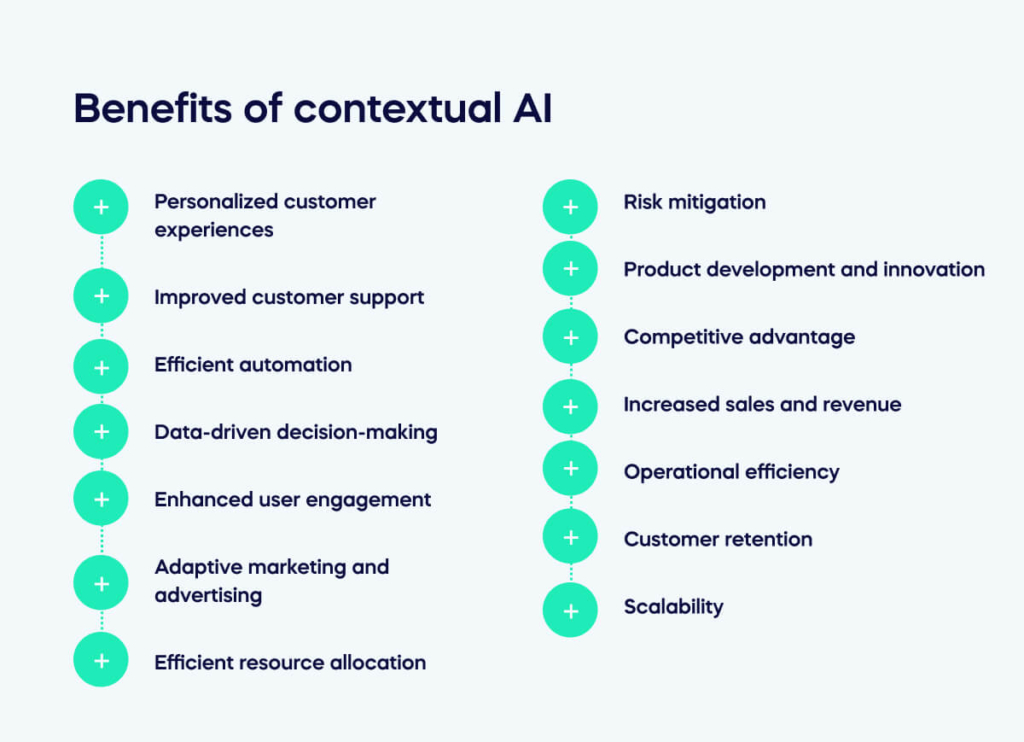
Benefits of contextual AI
Leveraging contextual AI can offer a range of significant business benefits, enhancing efficiency, customer satisfaction, and competitiveness:
Personalized customer experiences
Businesses can offer highly personalized experiences to their customers. Companies can deliver tailored product recommendations, content, and support by understanding customer preferences and behavior, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Improved customer support
The technology understands the context of customer inquiries and provides relevant and timely solutions. This reduces response times, minimizes errors, and increases the overall quality of customer service.
Efficient automation
Routine and repetitive tasks can be automated more effectively by considering the context of each task. Some benefits include operational efficiency, business resilience, reduced costs, and faster response times.
Data-driven decision-making
Vast amounts of data can be analyzed and interpreted to provide valuable insights and recommendations. Better-informed decision-making is enabled across various aspects of the business, from marketing strategies to supply chain management.
Enhanced user engagement
Offering context-aware content and interactions enables businesses to maintain higher levels of user engagement and attention levels. This approach can increase user retention rates and more interaction with products and services.
Adaptive marketing and advertising
Increasingly targeted and relevant marketing and advertising campaigns can be delivered with contextual AI. Businesses can adjust their messages and offerings in real-time based on user behavior and context, improving the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
Efficient resource allocation
Contextual AI can optimize resource allocation in staffing, inventory management, and production scheduling, leading to cost savings and improved resource utilization.
Risk mitigation
In industries like finance and healthcare, contextual AI can help identify potential risks and fraud in real-time. Taking a proactive approach can result in better risk management and loss prevention.
Product development and innovation
Contextual AI can analyze market trends, customer feedback, and competitive landscapes to inform product development and innovation strategies. New products and features will subsequently align with customer needs and market demands.
Competitive advantage
Companies that effectively leverage contextual AI can gain a competitive edge by delivering superior customer experiences, making more informed decisions, and staying ahead of industry trends.
Increased sales and revenue
Personalized recommendations and context-aware marketing can drive higher conversion rates and increased sales. Contextual AI can identify cross-selling and upselling opportunities, leading to revenue growth.
Operational efficiency
Businesses can achieve greater efficiency, reduce human errors, and save time and resources by automating routine tasks and adapting to changing circumstances.
Customer retention
Contextual AI helps build stronger customer relationships by providing timely and relevant interactions. Satisfied and engaged customers are more likely to remain loyal and continue doing business with the company.
Scalability
Contextual AI can help businesses handle increased workloads and customer interactions without a proportional increase in human resources. This scalability is valuable for growing companies.
Drawbacks of contextual AI
While contextual AI offers numerous advantages, it also comes with certain drawbacks and challenges that organizations need to be aware of:
Data privacy concerns
Contextual AI relies heavily on collecting and analyzing user data, which can raise concerns about data privacy and security. Mishandling or unauthorized access to this data can lead to privacy breaches and legal issues.
Data bias
AI systems can inherit biases present in the data they are trained on. This can result in unfair or discriminatory outcomes, particularly in contexts where historical biases exist.
Complex implementation
Developing and implementing contextual AI systems can be complex and resource-intensive. Businesses must invest in technology, data infrastructure, and expertise to fully realize the benefits.
Lack of transparency
Some contextual AI models, especially deep learning models, are considered “black boxes,” making it challenging to understand how they arrive at their decisions. This lack of transparency can be a barrier to trust and accountability.
Training data availability
For AI systems to operate effectively in various contexts, they require diverse and high-quality training data. In some cases, obtaining such data can be challenging and costly.
Integration challenges
Integrating contextual AI into existing systems and workflows can be difficult, especially in legacy environments. Compatibility issues and the need for substantial changes may arise.
User adoption
Some users may be uncomfortable or resistant to interacting with AI systems, especially in situations where they prefer human assistance.
Security vulnerabilities
As with any technology, contextual AI systems can be vulnerable to cyberattacks and security breaches. Protecting these systems from threats is crucial.
Performance variability
The performance of contextual AI systems may vary depending on the quality and availability of data, as well as the complexity of the context. In some situations, AI may provide less accurate results.
Regulatory compliance
Adhering to data privacy regulations and ethical guidelines for AI can be challenging and may require significant effort to ensure compliance.
How contextual AI works with DAPs
Contextual AI works with digital adoption platforms (DAPs) to enhance the user experience, provide personalized guidance, and improve software adoption.
Here’s how contextual AI is integrated into DAPs:
User behavior analysis
Contextual AI within a DAP starts by monitoring and analyzing user behavior as they interact with software applications, websites, or other digital tools.
Data is collected on how users navigate, where they encounter challenges, and which features they use most or least. This data serves as the foundation for understanding user context.
Contextual understanding
The AI system uses Natural Language Processing (NLP), machine learning, and other techniques to make sense of the data. It seeks to understand the user’s context, needs, and preferences.
For example, if a user struggles to complete a task in a software application, the AI can identify the specific step where they are facing difficulties.
Personalized guidance
Contextual AI can provide real-time, personalized guidance to users. For instance, it can offer in-app tips, step-by-step tutorials, or interactive walkthroughs tailored to the user’s context.
The guidance is designed to address the user’s immediate needs and help them overcome any obstacles they encounter while using the software.
User assistance
When users interact with the software, the contextual AI can detect when they need help and offer assistance proactively. This can include context-aware pop-ups, tooltips, or chatbot interactions.
The AI can also answer user questions, provide troubleshooting guidance, or route users to relevant resources.
User feedback and learning
Contextual AI in DAPs learns from user interactions and feedback. If a user finds a particular piece of guidance helpful or unhelpful, the AI system adapts and refines its recommendations.
Over time, the AI can improve its understanding of user contexts and assist more effectively.
Continuous improvement
DAPs with contextual AI are designed for continuous improvement. They can monitor user adoption rates, track the effectiveness of guidance, and identify areas where the software needs enhancements.
Based on these insights, DAPs can suggest improvements to the software, such as feature updates, redesigns, or additional training materials.
Contextual AI vs contextual intelligence
Contextual AI specifically involves AI technologies that process data and context to provide context-aware insights or assistance.
Meanwhile, contextual intelligence is a more general concept related to understanding and acting appropriately within a given context. This can involve both human and artificial intelligence.
Contextual AI is a subset of contextual intelligence, focusing on the AI aspect of context-aware decision-making and assistance.
Contextual AI and contextual intelligence can work in tandem.
Contextual AI provides the ability to process and analyze data quickly and accurately within a given context, while human intelligence contributes nuanced understanding, ethical reasoning, and creative problem-solving.
By combining these strengths, organizations can make more informed and effective decisions in a wide range of scenarios:
Enhancing human decision-making
Contextual AI can provide valuable insights and recommendations to support human decision-making. For example, AI systems can analyze complex data, identify patterns, and offer data-driven suggestions within a specific context, helping individuals make more informed choices.
Automating routine tasks
Contextual AI can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human intelligence for more complex and creative problem-solving. This automation is especially valuable in scenarios where repetitive actions must be taken within a specific context.
Improving efficiency
Organizations can improve efficiency and reduce errors by leveraging AI to handle tasks requiring context awareness. Contextual AI can quickly process and respond to contextual information, leading to faster and more accurate outcomes.
Handling large data volumes
In contexts with an overwhelming amount of data to process, contextual AI can sift through and extract relevant information, making it easier for humans to make sense of complex situations.
Learning from human intelligence
Contextual AI systems can learn from human intelligence and user interactions. Over time, they can adapt and improve their contextual understanding based on feedback and data collected from human users.
Providing real-time assistance
In situations where immediate responses and actions are crucial, contextual AI can rapidly analyze data in real-time, making it valuable for applications like fraud detection, cybersecurity, and dynamic customer support.
Enhancing user experience
Contextual AI can improve user experiences by offering personalized, context-aware recommendations and assistance. This is particularly important in digital adoption platforms, chatbots, and virtual assistants.
Complementing human judgment
While contextual AI can excel at data-driven decisions within a specific context, human judgment remains essential for complex, nuanced, ethical decision-making involving moral or emotional considerations.
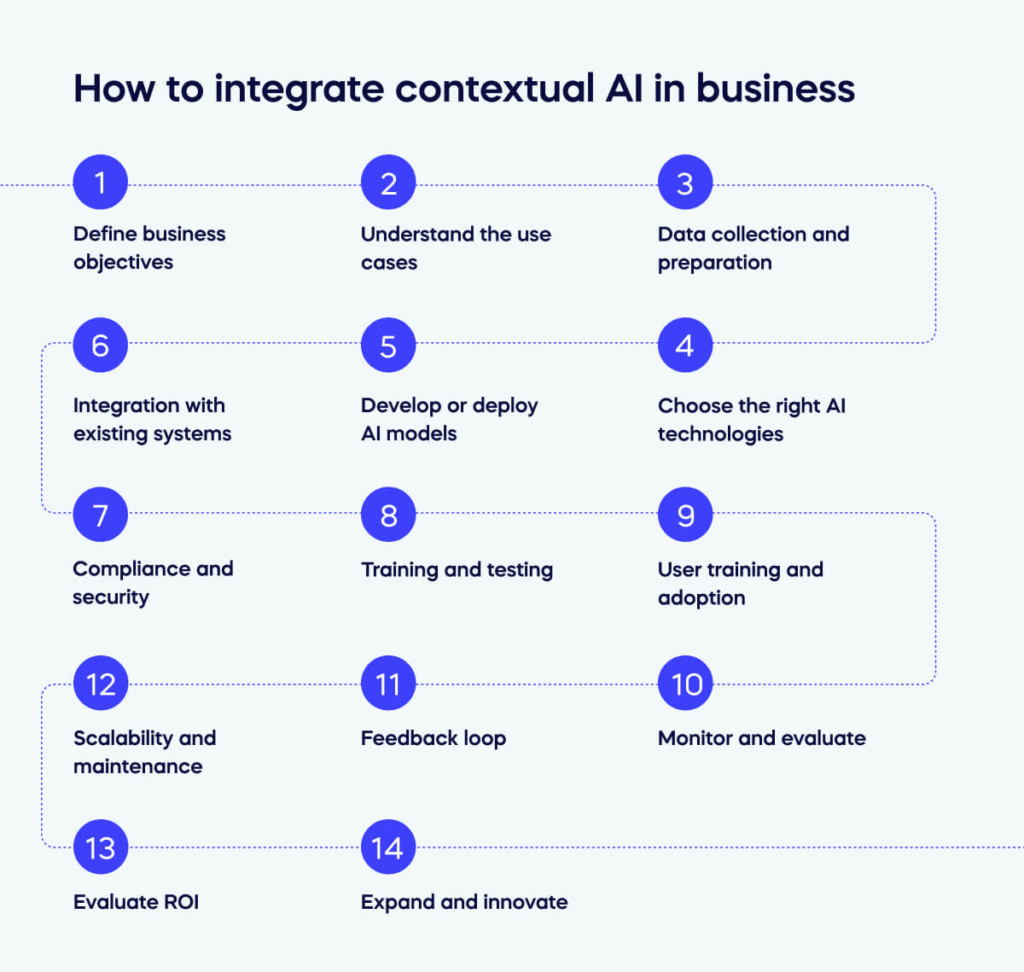
How to integrate contextual AI in business
Integrating contextual AI into a business involves a systematic approach to ensure the successful adoption and utilization of AI technologies in various business processes.
Here are the key steps to integrate contextual AI into your business:
Define business objectives
Start by identifying specific business objectives and goals that contextual AI can help address. These could include improving customer service, optimizing operations, enhancing user experiences, or increasing sales.
Understand the use cases
Identify specific use cases where contextual AI can be applied to achieve your desired objectives. These include chatbots for customer support, predictive equipment maintenance, or personalized marketing recommendations.
Data collection and preparation
Ensure you have access to the necessary data for training and operating your contextual AI systems. Data collection and preparation are critical to the success of AI models. Clean, structured, and relevant data is essential.
Choose the right AI technologies
Select the appropriate AI technologies that align with your use cases. For contextual AI, this might include natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, or deep learning, depending on the nature of the data and tasks.
Develop or deploy AI models
Depending on your resources and expertise, you can either develop AI models in-house or deploy pre-built AI solutions. Many AI platforms and frameworks are available that can expedite the development process.
Integration with existing systems
Ensure seamless integration of contextual AI into your existing business systems, such as CRM, ERP, and customer databases. This may involve building custom connectors or leveraging APIs.
Compliance and security
Address data privacy, security, and compliance concerns. When dealing with sensitive data, implement robust security measures and comply with relevant regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA.
Training and testing
Train your AI models on relevant data and test them thoroughly to ensure they perform as expected. Iterate and refine the models based on performance feedback.
User training and adoption
Educate your employees or end-users about the new AI systems. Train them to use and interact with the AI effectively and provide ongoing support.
Monitor and evaluate
Continuously monitor the performance of your contextual AI systems. Set up key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to evaluate their impact on your business objectives.
Feedback loop
Establish a feedback loop to collect user feedback and adapt your contextual AI systems accordingly. User input can be invaluable in refining AI models and improving user experiences.
Scalability and maintenance
Ensure that your AI systems can scale as your business grows. Regularly update and maintain your models and technology stack to stay current with advances in AI.
Evaluate ROI
Calculate the return on investment (ROI) of your contextual AI implementation. Determine whether it achieves the desired business objectives and make adjustments as necessary.
Expand and innovate
As you gain experience and confidence in contextual AI, consider expanding its use across various departments and exploring new applications to gain a competitive edge.